Introduction
This article describes how to build a sample service using Go micro in step by step fashion. Micro addresses the key requirements for building microservice systems. It takes the microservice architecture pattern and transforms it into a set of tools which act as the building blocks for scalable platforms
Installation
Install Go-Micro using the following commands
go get github.com/micro/go-micro
go get github.com/micro/micro
Initialization
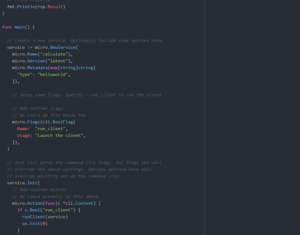
A service is created like so using micro.NewService.
![]()
Go Micro also provides a way to set command line flags using micro.Flags
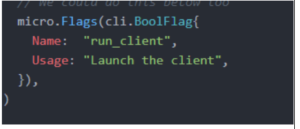
To parse flags use service.Init. Additionally access flags use the micro.Action option.
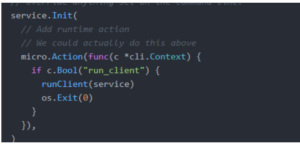
Go Micro provides predefined flags which are set and parsed if service.Init is called
Defining the API
We use protobuf files to define the service API interface. This is a very convenient way to st define the API and provide concrete types for both the server and a client.
Here’s an example definition.
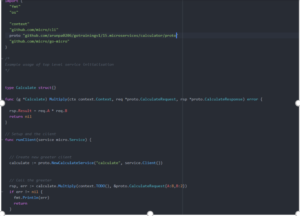
Calculate.proto
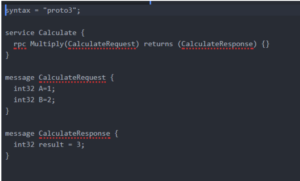
Here we’re defining a service handler called Calculate handler with the method Multiply which takes the parameter CalculateRequest type and returns CalculateResponse.
To compile proto file
protoc –proto_path=$GOPATH/src:. –micro_out=. –go_out=. Calculate.proto
Generate the API interface
We use protoc, protoc-gen-go and protoc-gen-micro to generate the concrete go implementation for this definition.
go get github.com/golang/protobuf/{proto,protoc-gen-go}
go get github.com/micro/protoc-gen-micro
The types generated can now be imported and used within a handler for a server or the client when making a request.
Here’s part of the generated code.
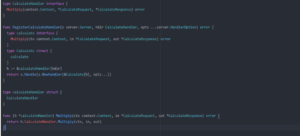
Implement the handler
The server requires handlers to be registered to serve requests. A handler is an public type with public methods which conform to the signature func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, rsp interface{}) error.
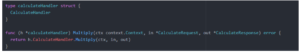
Here’s an implementation of the handler.

The complete service
main.go
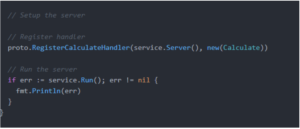
You can run service using go run main.go and run client using go run main.go –run_client

